In today’s digital world, speed is everything. Whether you’re streaming a movie, loading a website, or managing a cloud-based application, performance matters. Two of the most important concepts in understanding digital performance are data latency and bandwidth. While they both impact how fast and smoothly data travels, they refer to very different things. Understanding the distinction can help you make better decisions in IT, networking, and even personal tech use.
What is Bandwidth?
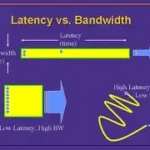
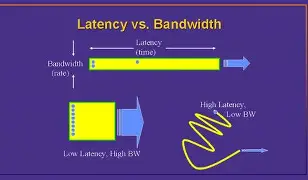
Think of bandwidth as the width of a highway. It measures how much data can travel over a network in a given amount of time, typically in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). The wider the highway, the more cars (or in this case, data packets) can pass through at once.
High bandwidth is crucial for data-heavy tasks like downloading large files, video conferencing, or streaming 4K video. More bandwidth means more capacity—but it doesn’t necessarily mean faster delivery of a single packet.
What is Data Latency?
Latency, on the other hand, is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from one point to another—like the time it takes for a car to get from point A to point B. It’s usually measured in milliseconds (ms). Low latency means less delay; high latency means more lag.
Latency becomes a critical factor in real-time applications like online gaming, stock trading, or VoIP calls, where even slight delays can cause noticeable issues.
Why the Confusion?
It’s easy to conflate the two. A high-speed internet connection (high bandwidth) doesn’t always mean a fast response (low latency). For example, you could have a fiber connection with gigabit speeds (excellent bandwidth), but if you’re connecting to a server halfway across the globe, you might still experience noticeable latency.
Real-World Example
Imagine you’re downloading a large file (say, a 2GB software update). High bandwidth means it downloads quickly. Now imagine you’re playing an online game. Even with great bandwidth, if your latency is high, your character might lag or respond slowly because every move you make takes too long to reach the game server and back.
So, Which Matters More?
It depends on the use case.
-
High bandwidth is essential for bulk data transfers, streaming, and large-scale downloads.
-
Low latency is critical for interactivity, real-time communication, and cloud-based control systems.
In an ideal setup, you want both—but knowing which matters more for your specific needs can help you choose the right technology and troubleshoot performance issues effectively.
In Summary:
Bandwidth is about how much.
Latency is about how fast.
And understanding the difference can help you optimize both performance and experience.